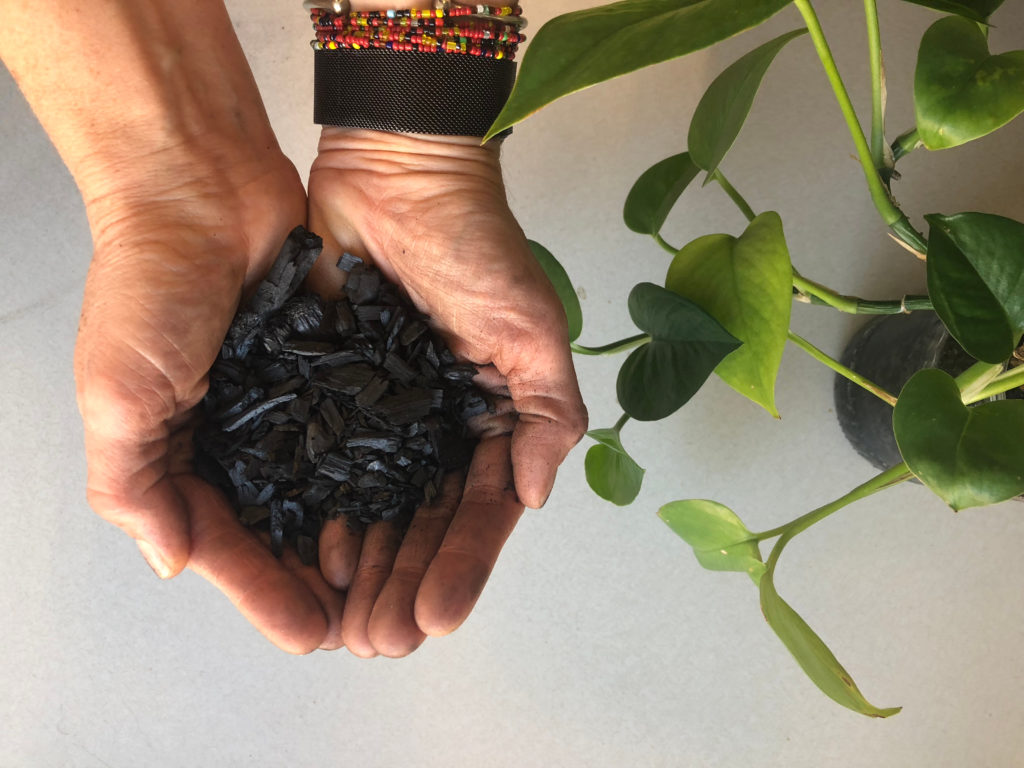
Biochar is a carbon-rich material produced during the pyrolysis process, which is a thermochemical decomposition of biomass at a temperature of ≤700°C in the absence or limited supply of oxygen. It is an important tool for carbon sequestration and has potential applications in agriculture, water filtration, and soil remediation.
Biochar made from agricultural waste can improve soil fertility and crop yields, while also reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It can also be used to filter water and remove contaminants such as heavy metals and organic pollutants. Additionally, biochar can be used to remediate contaminated soils by adsorbing harmful toxins.
Despite its many potential benefits, large-scale production of biochar faces challenges related to cost, scalability, and logistics. Additionally, more research is needed to optimize biochar production and understand its long-term effects on the environment.
Biochar Production
Biochar is produced through the process of pyrolysis, which is a thermochemical decomposition of biomass at a temperature of ≤700°C in the absence or limited supply of oxygen. There are many different types of pyrolysis reactors, but all follow the same general process.
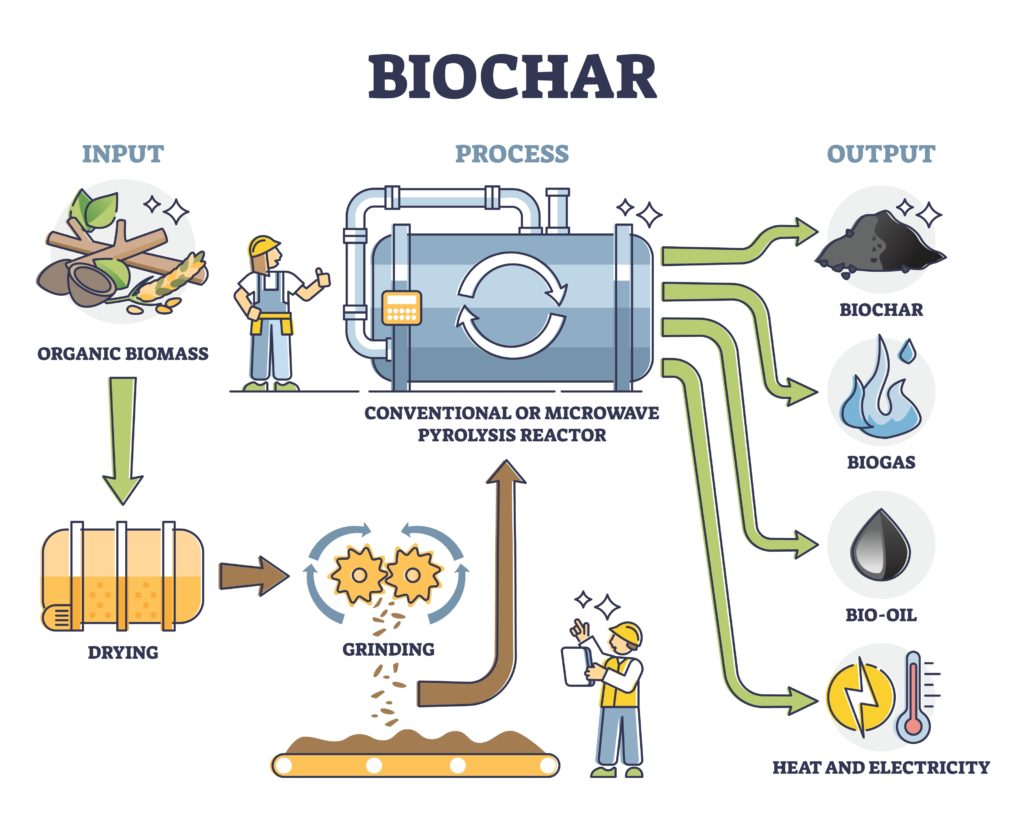
First, the biomass is fed into the reactor where it is heated to a high temperature. This causes the biomass to break down into its component parts: gases, liquids, and solid char. The gases and liquids are then removed from the reactor, leaving behind the biochar, which is subsequently stored or further processed.
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in the atmosphere to mitigate climate change. Biochar is a type of carbon sequestration that can be used to store carbon in the soil. When mixed with compost and applied to agricultural land, biochar can help improve soil fertility and crop yields while also sequestering carbon.
When added to agricultural soils, it can help sequester atmospheric carbon by increasing the soil’s ability to hold organic material and nutrients. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions while also improving soil fertility and crop yields. In fact, some studies have shown that adding biochar to soils can double crop yields compared with traditional farming methods.
Water Filtration
Biochar can be used as a water filtration system due to its high surface area and ability to adsorb contaminants. When placed in a water filter, biochar can remove heavy metals, organic pollutants, and other toxins from water. This makes it an effective tool for improving water quality.
Soil Remediation
Biochar can also be used to remediate contaminated soils. By adsorbing toxins and pollutants, biochar can clean up contaminated sites. This makes it an effective tool for restoring polluted land.
Compost & Biochar
Biochar is often used in combination with compost. Compost is a type of organic matter that can be added to soils to improve plant growth. When biochar and compost are mixed together, they can create a powerful tool for sequestering carbon, improving soil fertility, and increasing crop yields.
Carbon Sink
A carbon sink is a type of carbon sequestration that removes carbon from the atmosphere and stores it in a long-term reservoir. Biochar can be used as a carbon sink by sequestering atmospheric carbon in soils. This helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow the rate of climate change.
Biochar in Stock Fodder
In addition to its use in agriculture, biochar can also be used as a feedstock for livestock. When mixed into cattle feed, it has been shown to increase the growth and weight of cattle. This makes it an important resource for the livestock industry. This is particularity relevant as it pertains to the production of methane, a greenhouse gas, in livestock.
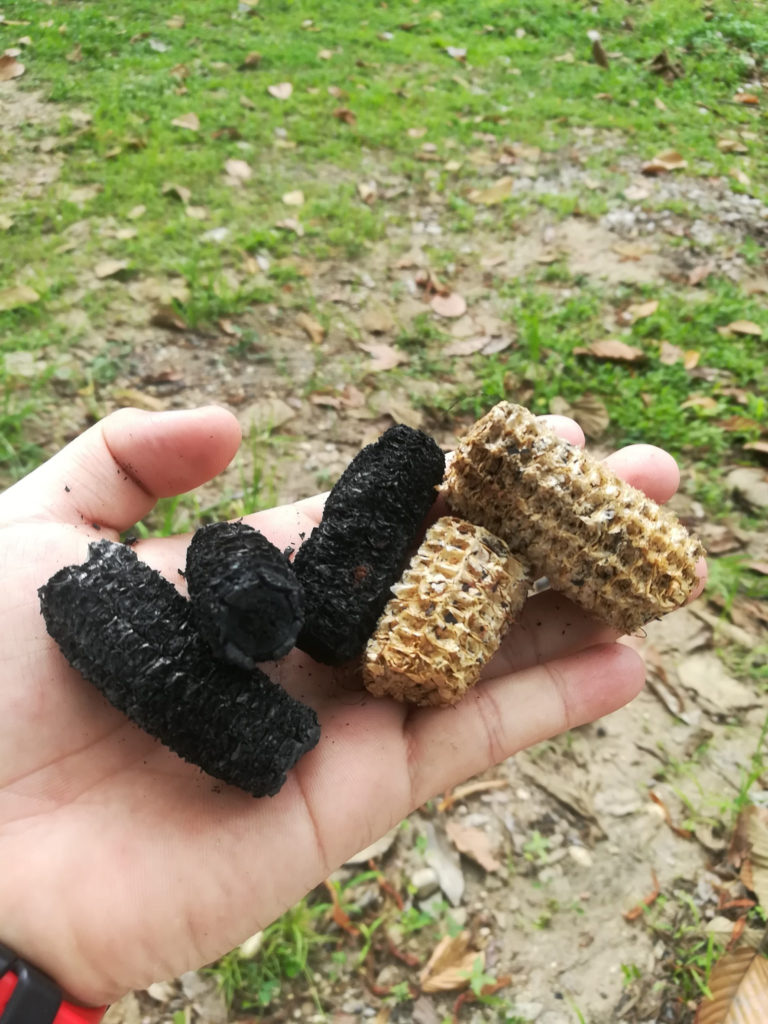

Climate Change Mitigation
As a type of carbon sequestration, biochar has the potential to mitigate climate change. By capturing and storing atmospheric carbon in soils, it can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow the rate of climate change.
Climate Change Adaptation
It can also help farmers adapt to climate change. As weather patterns become more erratic, biochar can help improve soil fertility and increase crop yields. This makes it an important tool for farmers who are struggling to adapt to a changing climate. Its use in agriculture can lead to a positive feedback loop that reinforces itself, resulting in increased carbon sequestration, improved crop yields and more.
Carbon Credits & Biochar
Carbon credits or carbon offsets are tradable certificates that represent the right to emit one metric ton of carbon dioxide or another greenhouse gas. Biochar is eligible for the generation of carbon credits under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Clean Development Mechanism. This means that biochar projects can earn carbon credits that can be sold to offset greenhouse gas emissions.
CO2 Removal Certificates
CO2 Removal Certificates are a type of carbon credit that can be generated from biochar projects. These certificates represent the removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and can be sold to offset emissions.

